Diploma in Massage Therapy
MODULE 1
What You Will Learn In This Course
- Discuss the history and evolution of massage therapy
- Outline the physical, mental and emotional benefits of massage therapy
- Explain the causes, types and management of chronic pain
- Outline the important principles of sports massage
- Discuss the benefits and risks of hydrotherapy and thermotherapy in pain management
- Identify some of the important warnings and contraindications related to deep tissue massage
- Explain how to choose hot stone massage equipment and stones
- Outline the benefits of prenatal and postnatal massage
- Describe different methods and techniques used in reflexology
- Explain how the lymphatic system is affected by lymphatic drainage massage
- Discuss the establishment, management and marketing of a massage therapy business
MODULE 1
Learn how massage therapy can improve your clients’ physical and mental health in this online diploma course.
Learning Outcomes
- Outline the important principles of sports massage.
- Explain the essential guidelines for using sports massage.
- Recognise the essential pointers for stretching safely and effectively.
- Identify basic stretches and techniques used in Thai massage.
- Recall specific stretches used only in Thai massage.
- Explain the fundamental ideas about safety and contraindications in Thai massage.
- Discuss the fundamental concepts and methods for hot stone massage.
- Describe the essential guidelines for choosing hot stone massage equipment and stones.
- List hot stone massage techniques.
- Describe how hot stone massage is integrated with other modalities.
Introduction to Massage Therapy
- History and Evolution of Massage Therapy.
- Types of Massage Therapy: An Overview.
- The Benefits of Massage Therapy.
- The Role Of A Massage Therapist.
- Professional Ethics And Scope Of Practice.
- Laws, Regulations, and Ethics in Massage Therapy.
History and Evolution of Massage Therapy

Ancient Civilizations’ Use of Massage for Healing
Massage treatment was predominantly used in ancient Egypt to promote relaxation and general health and fitness. Additionally, ailments and injuries were treated with it. Egyptian hieroglyphics have massage treatment imagery, and some tombs even have artwork of the procedure.
Similarly, massage treatment was used in ancient China to treat various medical ailments. Chinese people created the “tuina” system of massage treatment, founded on traditional Chinese medicine theories. Pressure points and meridians enhance the body’s qi or energy flow in tuina.
Ayurvedic medicine, which was exercised in India, included massage treatment. The promotion of health and wellness is the goal of Ayurveda, a traditional Indian medical system that achieves this through massage treatment and natural therapies. The balancing of the body’s energy and promotion of recovery are achieved in Ayurvedic massage with oils and herbs.
The Greeks also acknowledged the advantages of massage treatment. The founder of modern medicine, Hippocrates, discussed the advantages of massage treatment in his medical writings. He thought massage treatment might aid in boosting circulation and encouraging recovery.
Techniques for Relaxation and Healing
Swedish massage is a type of massage treatment created in the 19th century by Swedish physician Per Henrik Ling. Long strokes, kneading, and friction were used in Swedish massage to enhance circulation and encourage relaxation.
Western society began to adopt massage treatment more broadly in the 20th century. In addition to promoting relaxation and general well-being, it was used to cure ailments and injuries.
Athletes first used massage treatment in the United States to prevent and recover injuries. Spas, hospitals, and clinics are among the various places where massage therapy is practiced nowadays.
Types of Massage Therapy: An Overview
Since ancient times, people have used massage therapy, a common supplementary medicine, to induce relaxation, ease muscular tension, and enhance general health and wellness. There are several massage treatment methods and techniques, each with special advantages and applications. An overview of some of the most popular forms of massage treatment is provided in this module.
Swedish Bodywork

The most popular kind of massage treatment is Swedish. On the muscles’ outer layers, it uses lengthy strokes, kneading, and circular motions. Swedish massage helps to enhance circulation, reduce muscular tension, and encourage relaxation. It is a fantastic option for anyone searching for a soothing, full-body massage or new to massage treatment.
Massage with Deep Tissue

A stronger type of massage treatment is deep tissue massage. Slow, deep strokes are used to target the deeper levels of muscle tissue. Pain relief and reduction of chronic muscular tension are achieved with deep tissue massage. It is frequently advised for persons with particular muscular tension or stiffness in such locations.
Sports Massage
Athletes may avoid and treat injuries with the aid of sports massage. Various treatments, such as deep tissue massage and stretching, are used to enhance sports performance and avoid injuries. Sports massage is also utilised to hasten injury recovery for sportsmen.
Warm Stone Massage

With a hot stone massage, heated stones are used to aid with muscular relaxation. The stones are applied to certain body parts while receiving massage therapy to encourage relaxation and ease muscular tension. Anyone who appreciates heat treatment and wants a soothing full-body massage may consider a hot stone massage.
Massage with Aromatherapy

To improve the massage experience, aromatherapy massage uses essential oils. To induce relaxation and enhance general well-being, essential oils are added to the massage oil or lotion and used in massage techniques. Anyone who appreciates the advantages of essential oils and wants a soothing, full-body massage might consider an aromatherapy massage.
Types of Massage Therapy
Maternity Massage
A form of massage treatment known as the prenatal massage is created especially for pregnant women. It comprises a range of massage methods, including Swedish massage and deep tissue massage, to assist in reducing pregnancy-related aches and pains like back pain and oedema. Women seeking a secure and efficient method to ease the discomforts of pregnancy might consider prenatal massage.
Reflexology

Applying pressure to particular spots on the hands and feet is a key component of the reflexology massage technique. These locations are said to correspond to various bodily systems and organs. Both general health and well-being and the relief of particular symptoms and illnesses are supported by reflexology.
Shiatsu
Shiatsu is a form of massage treatment with Japanese roots. Similar to acupuncture, it involves applying finger pressure to certain body spots. Shiatsu treats particular illnesses and symptoms and advances general health and fitness.
Thai Bodywork
Thailand is where Thai massage, a form of massage treatment, first appeared. To enhance general health and wellness, it combines stretching with massage treatments. Given the amount of stretching and movement involved, Thai massage is sometimes compared to an aided form of yoga.
There are many different massage treatment modes and techniques available, to sum up. It is crucial to select a massage therapy method that is suited to your particular requirements and goals since each style of massage treatment has different advantages and applications. Massage treatment can help you reach your objectives and alleviate a certain illness or disease.
The Benefits of Massage Therapy
Since ancient times, massage treatment has been used to induce relaxation, ease powerful tension, and boost general health and wellness. The many advantages of massage treatment, which vary from physical to mental, have recently been proven by scientific studies.
Physical Advantages
Massage treatment’s major physical advantages are the reduction of powerful tension and discomfort. Increased blood course to the injured region, which assists in decreasing inflammation and encourages healing, can be achieved with a knead treatment. Additionally, it may aid in increasing flexibility, which makes it simpler to move around and carry out daily tasks.
Also, massage handling may help in better circulation, which is advantageous for the entire body. Increased circulation can facilitate the removal of waste materials and toxins from the body and the more efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. Massage may aid in the cure of some diseases and raise general wellness and fitness.
The ability of massage treatment to strengthen the immune system is another physical advantage. The activity of natural killer cells, white blood cells that aid in the defence against viruses and other pathogens, rises during massage treatment.
Benefits to the Mind and Emotions
Massage treatment has various emotional, mental and physical advantages. It has been demonstrated that massage treatment helps lower tension and anxiety, which can improve general health and wellness.
Sleep quality is another aspect of massage treatment that may aid general health and well-being. Massage treatment can enhance the quantity and quality of sleep by encouraging relaxation and lowering tension and anxiety.
Other Advantages
- Relief from headaches: Massage treatment can assist with headaches and migraines by easing shoulder and neck tension.
- Support for digestion: Massage treatment helps stimulate the digestive system, which can reduce constipation and other digestive problems.
- Recovery from injuries and injury prevention: Massage therapy can help avoid injuries by increasing the range of motion and flexibility. Additionally, it hastens the healing process following an accident.
- Posture improvement: Massage treatment can aid with posture by easing muscle tension and encouraging relaxation.
- Lymphatic drainage: Massage treatment can assist in fostering lymphatic drainage, which can aid in lessening oedema and strengthen the immune system.
The Role of a Massage Therapist
Massage therapists are responsible for imparting knowledge regarding the advantages of receiving a massage therapy treatment, in addition to providing said treatment itself, and teaching patients how they can achieve wellness. They may recommend enhancing your eating habits, way of life, and overall health and wellness.
Massage therapists must also uphold this duty to provide their customers with a safe and professional atmosphere. This involves ensuring their massage treatment clinic is sanitary, cosy, and clean. They must also uphold client confidentiality and follow ethical norms of conduct.
Spas, wellness centres, hospitals, and private practices are just a few places where massage therapists can work. Additionally, they could offer mobile massage therapy services, going to customers’ residences or places of business to give massage therapy treatments.
Authorisation and Practises
A massage therapist’s job also includes continual education and career development. The most recent research and advancements in massage therapy must be kept up to date by massage therapists, who must continue to grow their knowledge and abilities through workshops, seminars, and other learning opportunities.
To become massage therapists, one must complete a thorough education programme combining classroom learning with practical practice. However, specifics may vary from state to state or country to country. Becoming a massage therapist often involves finishing predetermined training hours and passing a licensing or certification exam.
Massage therapists who have obtained their licence or certification must uphold the moral requirements of their line of work to keep it and continue their education and professional development. This guarantees that they are current with the most recent advancements in the industry and are giving their clients safe and effective massage therapy treatments.
Therefore, the essential responsibility of any masseuse is to provide their clients with safe yet beneficial massages that raise comfort levels through promoting relaxation while reducing muscular discomforts. To attain these goals, they employ many approaches. They advise modifications in nutrition, exercise routines, and atypical aspects of everyday life to improve the health and wellness of their patients. Maintaining a safe and professional atmosphere for clients requires massage therapists to follow ethical standards of practice. Also, they ensure their professional advancement and avail themselves of prospects for continuous learning.
Professional Ethics and Scope of Practice
- Unless there is a legal necessity to divulge the information, massage therapists must keep all client information secret.
- Before beginning any massage therapy treatment, massage therapists must get the client’s permission. This involves outlining the course of therapy and seeking agreement before using any particular methods or procedures.
- Massage therapists must maintain professional boundaries with their customers and avoid any behaviour that might be deemed improper or unethical.
B. Areas of Practice
Massage therapists must practise only within the parameters of their scope of practice because they are not qualified to diagnose or treat medical disorders. The following are some fundamental guidelines for a massage therapist’s scope of practice:
- When clients’ symptoms or illnesses fall beyond their territory, massage therapists must refer them to a licensed healthcare provider.
- Massage therapists must create a treatment plan tailored to each client’s requirements and goals.
- Massage therapists must accurately and thoroughly document the progress of their patient’s treatments.
- Continued education is essential for massage therapists to keep current with changes in the industry and further their professional growth.
- Massage therapists may deliver safe and efficient massage therapy treatments suitable for each client’s requirements and goals by maintaining professional ethics and scope of practice rules.
Laws, Regulations and Ethics in Massage Therapy
While adhering to the highest standards of professionalism and ethical behaviour, these principles will assist massage therapists in providing safe and effective treatments that fit each client’s needs and goals.

The requirements for certification or licensing and guidelines for advertising and selling massage therapy services may be part of these laws and regulations. The therapists profession’s moral and legal standards must be followed; thus, massage therapists must be informed of these laws and guidelines.
Anatomy and Physiology

- The Skeletal System
- The Muscular System
- The Nervous System
- The Circulatory System
The Skeletal System
Bones have different shapes and sizes to serve particular functions, such as the long bones in the arms and legs that support the body and help with movement and the flat bones in the skull that protect the brain from outward forces as the brain is so delicate.
iii. Cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage is found in the joints, nose, and trachea.
- Fibrocartilage can be discovered in the intervertebral discs and the knee meniscus.
- Elastic cartilage is found mainly in the larynx, the outer part of the ear
Tendons, on the other hand, connect muscles to bones, allowing for movement of the body. They are also made up of tough, fibrous tissue and are responsible for transmitting muscle contraction to which they are attached.
Diseases Affecting the Skeletal System
A human bone is much like any other because it can get damaged or ill. Bones tend to become more fragile and weaker when affected by disorders like Osteoporosis which may cause an increased risk of bone fracture, and joint pain alongside stiffness and inflammation are classic symptoms of arthritis.
Other diseases involving the skeletal system include osteogenesis imperfecta, a sequence distract that causes toffee bones, and osteomyelitis, a bacterial contagion of the bone.
To maintain a sound system, it is important to engage in regular physical activity and to feed a balanced diet that includes plentifulness of calcium and vitamin D. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, and strength training in helping to build and maintain bone density while stretching and flexibility exercises put up services to improve articulate mobility and reduce the lay on the line of injury. Avoiding smoking and excessive intoxicant consumption can help protect the skeletal system.
The system is a complex and essential human body part. It keeps us alive by preventing damage to our vital organs, facilitating movement, producing blood cells, storing minerals, and keeping us hydrated. The skeleton’s strength and adaptability come from the network of ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and bones. Consistent physical activity is essential for bone wellness at its best.
The Muscular System
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles attached to the skeleton allow us to move our limbs and other bodily parts voluntarily. To create movement, they function in pairs, with one muscle contracting while the other relaxes. Skeletal muscles are striated, meaning they seem to be striped under a microscope. Additionally, we have conscious control over them, which enables us to direct how they move using our neural system.
Smooth Muscles
The walls of internal organs, including the stomach, intestines, and blood arteries, all include smooth muscles. They are in charge of involuntary movements like the contraction of blood vessels or the passage of food through the digestive tract. Organ muscles are not striated like skeletal muscles and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac Muscles
Blood is pumped throughout the body by cardiac muscles, which are located in the heart. Like skeletal muscles, they are likewise striated, but an involuntary process controls them. The ability of cardiac muscles to stimulate themselves and contract rhythmically without help makes them special.
Myofibrils
Myofibrils are known as the building blocks of muscle fibres. They make up all muscles. Actin and myosin, two proteins in myofibrils, work together to cause muscle contractions. A muscle’s strength increases with the number of its fibres.
Hypertrophy
Muscles may also adapt to different kinds of exercise via hypertrophy. Muscles enhance their strength and stamina in response to stress by producing more and bigger muscular fibres. This process occurs during strength training.
Movement
To create movement, the skeletal system and muscular systems collaborate. Strong tendons, fibrous connective tissue, are how muscles are connected to bones. According to nervous system instruction, a muscle’s contraction pushes on the bone to which it is linked, moving it forward or backwards.
Maintaining a Healthy Muscular System
The muscular system is essential for creating movement and stabilising and defending the body. To keep joints from becoming hurt when exercising, muscles stabilise the joints. Additionally, it protects organs vulnerable to any kind of external pressure.
However, no matter how protected, the musculoskeletal system is still vulnerable to injury or diseases. Strains, sprains, and tears in muscles are commonplace. It happens due to overuse or stress. Movement and function can also be damaged by diseases of the muscles, such as muscular dystrophy and myasthenia gravis.
Consistent exercise and a protein-rich diet may help to maintain muscle. Studies have shown that regular stretching exercises positively affect muscular function and help prevent injuries.
The muscular system is a complicated and essential human body component that enables mobility, stability, and protection. Actin and myosin-containing muscle fibres make up the skeletal and smooth muscles, which all cooperate to create movement.
To move, muscles must cooperate with the skeletal system, which they accomplish by attaching via tendons to bones. Maintaining a healthy muscular system requires regular exercise and a protein-rich diet.
The Nervous System
Your neurological system influences every part of your health, including:
- Mind, heart, brain, and soul.
- Actions like maintaining equilibrium and synchronisation.
- The senses and the mental processing of what you take in via them: sight, sound, taste, and touch.
- Relationships between sleep, health, and recovery.
- Rhythms of the heart and lungs.
- Reactions to trying circumstances.
- How you feel in terms of digestion, hunger, and thirst.
- The maturation of the body and other physiological processes.
The Network of Nerves
The messages sent by various neuron types vary. Muscles respond to signals from motor neurons. Information gathered by your senses is processed and relayed to your brain by sensory neurons. Breathing, shivering, maintaining a steady heartbeat, and digesting food are all automatic bodily processes controlled by different types of neurons.
Divisions of the Nervous System
- The neurons, or nerve cells, found in each component are in the billions. Throughout the entire body, cells communicate with each other via electric signals.
- Both the brain and spinal cord make up what is known as the central nervous system (CNS), which through its unique messaging capabilities to various parts of our bodies, aids in ensuring proper functioning. Myelin is a protective covering around the nerves. Myelin protects the nerve and makes it safer from damage, and conveys signals along it.
- The somatic nervous system controls movements.
- The part of your neural system responsible for your automatic behaviours.
Common Causes of Nerve Injury
- Nerve damage from diabetes, an endocrine condition, is referred to as diabetic neuropathy. This issue often manifests itself in the limbs and might cause pain there.
- The incidence of nerve injury is a very familiar complication associated with lupus.
- Individuals diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis are at a heightened susceptibility for the onset of neuropathy nowadays.
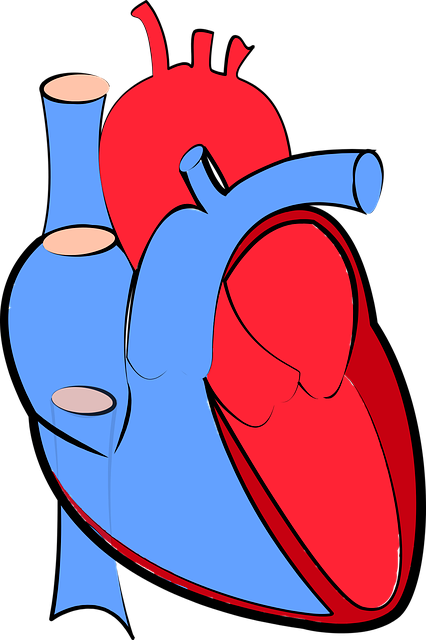
The Circulatory System
- The right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
After receiving oxygen from our lungs, blood goes into our heart’s left atrium before being distributed through arteries by contraction of 1st chamber left ventricle.
Types of Veins
To supply oxygenated blood to various organs in our bodies as well as returning deoxygenated blood back into our hearts, we have a system consisting primarily of 3 types of veins. They are:
Arteries

Their strong walls and musculature can stretch and contract to adapt to changes in blood flow.
Veins

Capillaries
Blood Components
The body’s defences against illnesses and other chemicals are aided by white blood cells.
The circulatory system controls core bodily functions such as temperature maintenance, waste removal, and nutrition delivery to cells. The system activates cells in the bloodstream to combat pathogens, playing a part in the immune response.
Maintaining a Healthy Cardiovascular System
To keep yourselves alive, a healthy heart must be maintained. Additionally, keeping a healthy weight and exercising regularly will make your heart healthy as a horse. And eventually, reduce the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease.
This process is a vital organic system that supplies the body with oxygen and nutrients. The heart, arteries, and blood comprise the cardiovascular system. The system transports oxygen and nutrients to cells, eliminates waste materials, and regulates core body temperature. To keep your system healthy, regular exercise, a good diet, no cigarette products, and moderate alcohol use are all musts.
Kinesiology
- Basic Principles of Kinesiology
- Joint Structure and Function
- Muscle Actions and Movements
- Posture and Gait Analysis
- Range of Motion and Flexibility
Basic Principles of Kinesiology
Basic Principles of Kinesiology
1. Specificity
Specificity is the first principle of kinesiology. According to this idea, the body will adjust to its unique demands. Rather than engaging in general physical exercise, someone who wishes to increase their running performance must train particularly for running-based exercise. This idea also holds for various forms of exercise, such as strength and endurance training.
2. Overload
Overload is the second principle of kinesiology. The body has to be stressed beyond its limits to improve, and so goes the thinking. More exercise is needed to enhance physical strength, stamina, and flexibility. Exercise frequency, length, or intensity can steadily increase to achieve this.
3. Progress
Progress is the third principal of kinesiology. According to this theory, the task must be gradually raised to continue progressing. As a result, the body is continually tested and forced to adjust to changing demands. Progress can be made by adding new exercises, adapting current ones, or progressively increasing the volume, duration, or frequency of exercise.
4. Reversibility
Reversibility is the fourth kinesiology principle. According to this theory, the adaptations acquired via training will be lost if the activity is stopped or diminished. If someone quits working out, they will gradually lose strength and muscle mass. This idea emphasises the significance of consistency in training and sustaining a consistent workout schedule.
5. Individuality
Individuality is the fifth governing principle of kinesiology. This idea acknowledges that every person is different and will react to exercise differently. Age, sex, genetics, and prior training are only a few factors that might affect a person’s response to physical activity. Therefore, programmes should be tailored to prioritise individuality.
6. Recovery
6. Recovery is the sixth principal of kinesiology. This idea emphasises the need to give the body enough time to rest between workouts. This involves getting enough sleep and food to support muscle recovery and energy storage replenishment. Injury and poor performance can result from overtraining or failing to give your body adequate time to recuperate.
7. Variety
7. Variety is the seventh principle of kinesiology. This theory argues that switching up your workouts and training techniques is critical if you want to keep improving. This may help you avoid becoming bored, keep you safe, and push your body in different ways.
Joint Structure and Function
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial Joints
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints are the three primary types of joints. Examples of fibrous joints that are immobile and kept together by fibrous tissue are the joints between the bones in the skull.
Cartilage-linked joints, including those between spinal vertebrae, have a relatively limited range of motion. Synovial joints are the most flexible and allow relatively unrestricted shoulder, hip, knee, and elbow movement.
Numerous parts of synovial joints work together to provide stability and motion. The joint is surrounded by the dense, fibrous tissue that makes up the joint capsule, which protects and supports the joint. The joint capsule contains synovial fluid, which helps lubricate and cushion the joint while it moves.
Articular Cartilage
Articular cartilage, also known as smooth cartilage or slippery cartilage, covers the bones at the joint. When moving, this cartilage reduces friction and absorbs stress. Ligaments, powerful bands of connective tissue that bind bones to one another and limit excessive joint movement, also stabilise the joint.
Muscles are vital for healthy joints because they adhere to bones through tendons and produce motion at the joint. Agonist muscles work in opposition to antagonist muscles with the help of synergistic muscles when acting across a joint, and agonist and antagonist are two types of muscle groups where the former leads to contraction and the latter results in relaxation. Together with the agonist’s muscles, synergist muscles create movement.
Joints are essential for movement, absorbing stress, and defending the body. The joints serve as shock absorbers during movements like running and leaping, lessening the force on the bones and preventing injuries.
Factors Affecting Joint Health and Diseases
Diseases and injuries may still affect joints. Cartilage deterioration is what causes arthritis which usually manifests as joint pains and inflammations while joint dysfunction could result due to an injury caused by a sprain or dislocation that damages its bones and ligaments.
A nutritious diet combined with frequent exercise is important for maintaining optimal joint health. Muscle development, joint stability, and injury avoidance are all aided by regular strength exercise. Stretching and other forms of joint mobility training may also help.
Therefore, joint mobility and structure are crucial to human movement. The locations on the body where two or more bones meet are known as joints, and they may be broadly categorised into three groups: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
The most typical form is a synovial joint, consisting of interconnected components that help with stability and mobility. Joint health depends on a number of lifestyle factors, including regular exercise, a good diet, and a stable weight.
Muscle Actions and Movements
Isotonic Muscle Action
Isotonic muscle action, which includes the contraction of muscles to create movement at the joints, is the first form of muscular action. Concentric and eccentric contractions are additional categories for isotonic muscular movements.
Muscles fully contract when they shorten during movements such as bicep curls causing complete contractions, but in weightlifting an eccentric contraction arises when muscles lengthen under tension such as during the downward phase of a bicep curl.
Isometric muscular activity, which includes muscle contraction without causing joint movement, is the second form of muscle action. Muscle contracts to preserve joint stability, like while doing a plank exercise; this is known as an isometric movement.
Flexion
The direction and orientation of muscle movements are another way to categorise them. These include rotation, circumduction, flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. Flexion happens when the joint angle is reduced, like when the elbow or knee is bent. Extension occurs when the joint angle rises, like when straightening the elbow or knee.
When a body part travels away from its midline, such as lifting the arms to the side, it is said to be abducted. And when a bodily component travels towards the body’s midline, such as when lowering the arms back down to the sides is called adduction movement.
When a body part rotates about its long axis, like when the head turns to gaze to one side, rotation occurs. This is called circumduction, when a bodily part travels circularly, such as creating circles with the arms.
Factors Affecting Muscular Actions/Maintenance
The neurological system, which delivers impulses to the muscles for beginning and governing movement, regulates muscular motions and activities. The neurological system collaborates with the muscular and skeletal systems to create movement and maintain posture.
However, diseases and injuries may still affect muscular actions and motions. Overuse, injuries, or underlying medical disorders may cause muscle strains, rips, and inflammation. Additionally, certain illnesses, including muscular dystrophy, may affect how well muscles work and cause mobility problems.
Regular physical exercise, a balanced diet, and enough sleep are necessary to maintain good muscular actions and motions. Stretching and mobility exercises may increase flexibility and range of motion, while resistance training can increase muscular strength and endurance.
Human movement and mobility depend on the activities and motions of the muscles. Based on their direction and orientation, they may be divided into numerous distinct categories. They entail the contraction and relaxation of muscles to cause movement at the joints.
The neural system coordinates with the muscular and skeletal systems to govern the actions and motions of the muscles. Regular physical exercise, a balanced diet, and enough sleep are necessary to maintain good muscular actions and motions.
Posture and Gait Analysis
Bad posture has the potential to cause backaches, joint dysfunctions & other related issues like neck pain or headaches. A therapy plan to address these problems may be created using posture analysis to identify areas of imbalance or weakness. Exercises to increase strength and flexibility, manual therapy to relieve stress, and good body mechanics and ergonomics instruction may all be part of the treatment.

Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Posture
- Gait analysis examines how a person moves when walking or running. A qualified expert may evaluate gait by seeing how the head, shoulders, arms, torso, hips, legs, and feet move concerning one another. Gait analysis may spot problems, including overpronation, supination, uneven leg lengths, and muscular imbalances or weakness.
- Gait analysis might be helpful for athletes trying to improve their performance or avoid injury. It may also establish a therapy plan and enhance functional movement for those with mobility problems or injuries.
- Gait and posture analysis may be done using a variety of instruments and methods. These include physical muscle testing, joints’ range of motion evaluation, visual observation, and computerised gait analysis systems. Computerised gait analysis systems use sensors and cameras to record and analyse data on how the body moves when walking or running. This may provide more complete details on time, symmetry, and joint angles.
- Analysis of posture and gait also includes prevention as a key component in addition to evaluation and therapy. Back discomfort, neck pain, and joint dysfunction may all be avoided by maintaining good posture and moving with the right body mechanics. Wearing supportive footwear, keeping a healthy weight, and participating in regular physical exercise all assist in improving posture and avoiding gait problems.
Range of Motion and Flexibility
Flexibility is necessary to keep up healthy movement patterns and prevent injuries. Injury risk may increase due to compensatory movement patterns caused by tight muscles and connective tissue. Stretching methods include proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching, dynamic stretching, and static stretching may all help you become more flexible.
Methods for Improving Flexibility/Range of Motion
Stretching
To extend the range of muscle and improve flexibility, static stretching includes maintaining a stretch for a certain amount of time, often 10 to 30 seconds.
To warm up the body and prepare it for exercise, dynamic stretching entails moving the muscles and joints through their complete range of motion, such as arm circles or leg swings. PNF stretching includes tightening and releasing the muscles during stretching to promote flexibility and range of motion.
Several different circumstances may impact flexibility and range of motion. As people age, their muscles and connective tissue naturally become less flexible with the lower range of motion.
Injuries and medical diseases like arthritis may also impact a range of motion and flexibility. Lifestyle choices like inactivity and bad posture may also cause reduced flexibility and range of motion.
Stretching Exercises
If you want to enhance the quality of your physical movement then it is important that you add some simple stretching exercises to your daily workout regimen as improving flexibility and range of motion is possible by strengthening the muscles along with connective tissue that encompasses the joints through resistance exercise.
Stretching and flexibility exercises should be done carefully to avoid damage. Never push yourself during a stretch or do it until you feel pain; always stretch softly. After warming up, stretching the body’s major muscle groups is important.
In addition to physical activity and stretching exercises, other therapies like foam rolling and massage therapy may also help to improve flexibility and range of motion. Massage therapy manipulates the muscles and connective tissue to improve circulation and lessen tension. Foam rolling is a method for reducing muscle and connective tissue tension and boosting flexibility.
Lesson Summary
- Massage treatment was predominantly used in ancient Egypt to promote relaxation and general health and fitness.
- The many advantages of massage treatment, which vary from physical to mental, have recently been proven by scientific studies.
- Massage treatment helps lower tension and anxiety, which can improve general health and wellness.
- The skeletal system is one of the most important systems in the human body.
- Bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons make up the skeletal system, which in turn provides the body with a warm and flexible theoretical account.
- Bones tend to become more fragile and weaker when affected by disorders like Osteoporosis which may cause an increased risk of bone fracture, and joint pain alongside stiffness and inflammation are classic symptoms of arthritis.
- To maintain a sound system, it is important to engage in regular physical activity and to feed a balanced diet that includes plenty of calcium and vitamin D.
- The muscular system is a vital human body component that enables mobility, stability, and defence. Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles all make up this system.
- Almost everything you do, say, or feel is controlled by your nervous system. Movement, thinking, and memory are only a few complex functions it regulates.
- The circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, and other materials throughout the body, which comprises a convoluted web of organs and veins. The heart, blood arteries, and systemic blood make up the system.
- Arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the body’s tissues.
- Blood vessels with the same size and different functions, called Veins, transport blood from the body’s tissues back to the heart.
- Capillaries are tiny, thin-walled blood channels that link veins and arteries.
- Platelets, plasma, and white and red blood cells make up blood.
- Kinesiology studies human movement and uses anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and psychological concepts to enhance athletic performance and avoid injuries.
- Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints are the three primary types of joints.
- A nutritious diet combined with frequent exercise is important for maintaining optimal joint health.
- The neurological system, which delivers impulses to the muscles for beginning and governing movement, regulates muscular motions and activities.
- Measuring the body’s alignment in static and dynamic situations is a component of posture analysis.
Learn how massage therapy can improve your clients’ physical and mental health in this online diploma course.

